SQL注入问题 SQL注入问题说的是:用户输入的信息中含有SQL语句关键字,和程序中的SQL语句进行字符串拼接,导致程序中的SQL语句改变了原意。(SQL注入问题是一种系统安全问题)
1 select * from t_user where name = 用户输入的用户名 and password = 用户输入的密码;
如果以上的SQL语句能够查询到结果,说明用户名和密码是正确的,则登录成功。如果查不到,说明是错误的,则登录失败。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ResourceBundle;import java.util.Scanner;public class JDBCTest02 { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("欢迎使用用户管理系统,请登录!" ); Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); System.out.print("用户名:" ); String loginName = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.print("密码:" ); String loginPwd = scanner.nextLine(); ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); Connection conn = null ; Statement stmt = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "select realname from t_user where name = '" +loginName+"' and password = '" +loginPwd+"'" ; rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); if (rs.next()) { String realname = rs.getString("realname" ); System.out.println("登录成功,欢迎您" + realname); } else { System.out.println("登录失败,用户名不存在或者密码错误。" ); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } finally { if (rs != null ) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (stmt != null ) { try { stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } } }
如果用户名和密码正确的话,执行结果如下:
如果用户名不存在或者密码错误的话,执行结果如下:
接下来,见证奇迹的时刻,当我分别输入以下的用户名和密码时,系统被攻破了:
1 select realname from t_user where name = 'sunwukong' and password = '123' ;
结果被SQL注入之后,SQL语句就变成这样了:
1 select realname from t_user where name = 'aaa' and password = 'bbb' or '1' = '1' ;
我们可以执行一下这条SQL,看看结果是什么?
解决SQL注入问题 导致SQL注入的根本原因是什么?只有找到真正的原因,问题才能得到解决。
最根本的原因是:Statement造成的。
Statement执行原理是:先进行字符串的拼接,将拼接好的SQL语句发送给数据库服务器,数据库服务器进行SQL语句的编译,然后执行。因此用户提供的信息中如果含有SQL语句的关键字,那么这些关键字正好参加了SQL语句的编译,所以导致原SQL语句被扭曲。
因此,JDBC为了解决这个问题,引入了一个新的接口:PreparedStatement,我们称为:预编译的数据库操作对象。PreparedStatement是Statement接口的子接口。它俩是继承关系。
PreparedStatement执行原理是:先对SQL语句进行预先的编译,然后再向SQL语句指定的位置传值,也就是说:用户提供的信息中即使含有SQL语句的关键字,那么这个信息也只会被当做一个值传递给SQL语句,用户提供的信息不再参与SQL语句的编译了,这样就解决了SQL注入问题。
使用PreparedStatement解决SQL注入问题:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ResourceBundle;import java.util.Scanner;public class JDBCTest03 { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("欢迎使用用户管理系统,请登录!" ); Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); System.out.print("用户名:" ); String loginName = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.print("密码:" ); String loginPwd = scanner.nextLine(); ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement pstmt = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "select realname from t_user where name=? and password=?" ; pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setString(1 , loginName); pstmt.setString(2 , loginPwd); rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); if (rs.next()) { String realname = rs.getString("realname" ); System.out.println("登录成功,欢迎您" + realname); } else { System.out.println("登录失败,用户名不存在或者密码错误。" ); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } finally { if (rs != null ) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (pstmt != null ) { try { pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } } }
用户名和密码正确的话,执行结果如下:
用户名和密码错误的话,执行结果如下:
尝试SQL注入,看看还能不能?根本原因是:bbb’ or ‘1’=’1 这个字符串中虽然含有SQL语句的关键字,但是只会被当做普通的值传到SQL语句中,并没有参与SQL语句的编译 。
关于使用PreparedStatement要注意的是:
带有占位符 ? 的SQL语句我们称为:预处理SQL语句。
占位符 ? 不能使用单引号或双引号包裹。如果包裹,占位符则不再是占位符,是一个普通的问号字符。
在执行SQL语句前,必须给每一个占位符 ? 传值。
如何给占位符 ? 传值,通过以下的方法:
pstmt.setXxx(第几个占位符, 传什么值)
“第几个占位符”:从1开始。第1个占位符则是1,第2个占位符则是2,以此类推。
“传什么值”:具体要看调用的什么方法?
如果调用pstmt.setString方法,则传的值必须是一个字符串。
如果调用pstmt.setInt方法,则传的值必须是一个整数。
以此类推……
PreparedStatement和Statement都是用于执行SQL语句的接口,它们的主要区别在于:
PreparedStatement预编译SQL语句,Statement直接提交SQL语句;
PreparedStatement执行速度更快,可以避免SQL注入攻击;(PreparedStatement对于同一条SQL语句来说,编译一次,执行N次。而Statement是每次都要进行编译的。因此PreparedStatement效率略微高一些。)
PreparedStatement会做类型检查,是类型安全的;
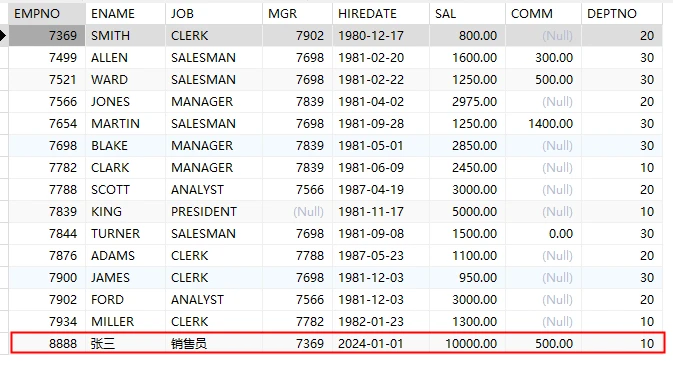
PreparedStatement的使用 新增操作 需求:向 emp 表中插入这样一条记录:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.time.LocalDate;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class JDBCTest04 { public static void main (String[] args) { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement pstmt = null ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "insert into emp(empno,ename,sal,comm,job,mgr,hiredate,deptno) values(?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)" ; pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setInt(1 , 8888 ); pstmt.setString(2 , "张三" ); pstmt.setDouble(3 , 10000.0 ); pstmt.setDouble(4 , 500.0 ); pstmt.setString(5 , "销售员" ); pstmt.setInt(6 , 7369 ); LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.parse("2024-01-01" ); pstmt.setDate(7 , java.sql.Date.valueOf(localDate)); pstmt.setInt(8 , 10 ); int count = pstmt.executeUpdate(); if (1 == count) { System.out.println("成功更新" + count + "条记录" ); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (pstmt != null ) { try { pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } } }
重点学习内容:如何给占位符 ? 传值。
修改操作 需求:将员工编号为8888的员工,姓名修改为李四,岗位修改为产品经理,月薪修改为5000.0,其他不变。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.time.LocalDate;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class JDBCTest05 { public static void main (String[] args) { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement pstmt = null ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "update emp set ename = ?, job = ?, sal = ? where empno = ?" ; pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setString(1 , "李四" ); pstmt.setString(2 , "产品经理" ); pstmt.setDouble(3 , 5000.0 ); pstmt.setInt(4 , 8888 ); int count = pstmt.executeUpdate(); if (1 == count) { System.out.println("成功更新" + count + "条记录" ); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (pstmt != null ) { try { pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } } }
执行结果如下:
删除操作 需求:将员工编号为8888的删除。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class JDBCTest06 { public static void main (String[] args) { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement pstmt = null ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "delete from emp where empno = ?" ; pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setInt(1 , 8888 ); int count = pstmt.executeUpdate(); if (1 == count) { System.out.println("成功更新" + count + "条记录" ); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (pstmt != null ) { try { pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } } }
执行结果如下:
模糊查询 需求:查询员工名字中第二个字母是 O 的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class JDBCTest07 { public static void main (String[] args) { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement pstmt = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "select ename from emp where ename like ?" ; pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setString(1 , "_O%" ); rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { String ename = rs.getString("ename" ); System.out.println(ename); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (rs != null ) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (pstmt != null ) { try { pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } } }
执行结果如下:
1 2 String sql = "select ename from emp where ename like '_?%'" ;pstmt.setString(1 , "O" );
由于占位符 ? 被单引号包裹,因此这个占位符是无效的。
分页查询 对于MySQL来说,通用的分页SQL语句:第pageNo页:limit (pageNo - 1)* pageSize, pageSize**
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class JDBCTest08 { public static void main (String[] args) { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement pstmt = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; int pageSize = 3 ; int pageNo = 2 ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "select ename from emp limit ?, ?" ; pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setInt(1 , (pageNo - 1 ) * pageSize); pstmt.setInt(2 , pageSize); rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { String ename = rs.getString("ename" ); System.out.println(ename); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (rs != null ) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (pstmt != null ) { try { pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } } }
执行结果如下:
blob数据的插入和读取 准备一张表:t_img,三个字段,一个id主键,一个图片名字name,一个img。
1 2 3 4 5 create table `t_img` ( `id` bigint primary key auto_increment, `name` varchar (255 ), `img` blob ) engine= innodb;
准备一张图片:
需求1:向t_img 表中插入一张图片。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class JDBCTest09 { public static void main (String[] args) { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement pstmt = null ; InputStream in = null ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "insert into t_img(img) values(?)" ; pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); in = new FileInputStream ("d:/dog.jpg" ); pstmt.setBlob(1 , in); int count = pstmt.executeUpdate(); System.out.println("插入了" + count + "条记录" ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (in != null ) { try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (pstmt != null ) { try { pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } } }
执行结果如下:
需求2:从t_img 表中读取一张图片。(从数据库中读取一张图片保存到本地。)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.InputStream;import java.io.OutputStream;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class JDBCTest10 { public static void main (String[] args) { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement pstmt = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "select img from t_img where id = ?" ; pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setInt(1 , 1 ); rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); if (rs.next()) { Blob img = rs.getBlob("img" ); InputStream binaryStream = img.getBinaryStream(); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream ("d:/dog2.jpg" ); byte [] bytes = new byte [1024 ]; int readCount = 0 ; while ((readCount = binaryStream.read(bytes)) != -1 ) { out.write(bytes, 0 , readCount); } out.flush(); binaryStream.close(); out.close(); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (rs != null ) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (pstmt != null ) { try { pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } } }
执行完毕之后,查看一下图片大小是否和原图片相同,打开看看是否可以正常显示。
JDBC批处理操作 准备一张商品表:t_product
1 2 3 4 create table t_product( id bigint primary key, name varchar (255 ) );
不使用批处理 不使用批处理,向 t_product 表中插入一万条商品信息,并记录耗时!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class NoBatchTest { public static void main (String[] args) { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement pstmt = null ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "insert into t_product(id, name) values (?, ?)" ; pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); int count = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= 10000 ; i++) { pstmt.setInt(1 , i); pstmt.setString(2 , "product" + i); count += pstmt.executeUpdate(); } System.out.println("插入了" + count + "条记录" ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (pstmt != null ) { try { pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("总耗时" + (end - begin) + "毫秒" ); } }
执行结果如下:
使用批处理 使用批处理,向 t_product 表中插入一万条商品信息,并记录耗时!注意:启用批处理需要在URL后面添加这个的参数:rewriteBatchedStatements=true
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class BatchTest { public static void main (String[] args) { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); String url = bundle.getString("url" ); String user = bundle.getString("user" ); String password = bundle.getString("password" ); long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement pstmt = null ; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "insert into t_product(id, name) values (?, ?)" ; pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); int count = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= 10000 ; i++) { pstmt.setInt(1 , i); pstmt.setString(2 , "product" + i); pstmt.addBatch(); } count += pstmt.executeBatch().length; System.out.println("插入了" + count + "条记录" ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (pstmt != null ) { try { pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("总耗时" + (end - begin) + "毫秒" ); } }
执行结果如下:
在进行大数据量插入时,批处理为什么可以提高程序的执行效率?
减少了网络通信次数:JDBC 批处理会将多个 SQL 语句一次性发送给服务器,减少了客户端和服务器之间的通信次数,从而提高了数据写入的速度,特别是对于远程服务器而言,优化效果更为显著。
减少了数据库操作次数:JDBC 批处理会将多个 SQL 语句合并成一条 SQL 语句进行执行,从而减少了数据库操作的次数,减轻了数据库的负担,大大提高了数据写入的速度。
DbUtils工具类的封装 JDBC编程六步中,很多代码是重复出现的,可以为这些代码封装一个工具类。让JDBC代码变的更简洁。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 package com.powernode.jdbc;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class DbUtils { private static String url; private static String user; private static String password; static { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.powernode.jdbc.jdbc" ); String driver = bundle.getString("driver" ); url = bundle.getString("url" ); user = bundle.getString("user" ); password = bundle.getString("password" ); try { Class.forName(driver); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } public static Connection getConnection () throws SQLException { Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); return conn; } public static void close (Connection conn, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs) { if (rs != null ) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (stmt != null ) { try { stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } }